2021-04-22, 18:21
How Many Homes Could You Power With Free Doughnuts?
Should you get a COVID vaccine? Yes, it will protect you AND protect others to help us move past this pandemic so we can get back to a more normal life. But wait! If you get vaccinated, you can also get a doughnut! At least that's the deal that Krispy Kreme Doughnuts is offering. Once you get your vaccine, you get a doughnut. Oh, it's not just one doughnut—it's one doughnut every day. That's a lot of doughnuts.
OK, so how about some physics estimations to go along with your tasty doughnut?
Let's say that all the Americans that have a COVID vaccine get (and eat) one doughnut a day. Of course eating food gives you energy to do stuff—that's how food works. So, suppose that all these humans eat their doughnut and then use the extra energy to peddle a stationary bike. All of these bikes are then connected to generators so that they feed into the power grid. What kind of power output would this produce?
The first thing we need is the number of doughnuts a day. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC) 63 million Americans have been fully vaccinated so far (as of April 7 2021). Oh, don't worry too much about the numbers—I'm going to do all my calculations in python so that you can change the values if that makes you happy. I'm also going to assume that all these people get their doughnut—every day.
Next, I need to know the amount of energy per doughnut. According to Krispy Kreme's site, a plain glazed doughnut is 190 Calories. But what the heck is a Calorie? Well, [the original calorie was created to describe changes in thermal energy for different substance](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calories. Then, later people used it to measure the amount of chemical energy your body can get from eating food. However, there is a problem. For some reason, all food labels list stuff in Calories—but these are really kilocalories. So, that doughnut has 190,000 calories. I guess it just sounds like it's too big of a number for people to consider eating.
There is another unit of energy—the joule. Since this is the preferred unit of energy for physicists, I'm going to use it. To convert between units, 1 calorie is equal to 4.184 joules. But what does this have to do with your everyday life? Let's consider something you might do without too much effort. Suppose you have a textbook on the floor and you pick it up to put it on a table. Since you are exerting a force on the book over some distance, you have to change the gravitational potential energy of that book. The change in gravitational potential energy is equal to the mass of the book (about 1 kilogram) multiplied by the local gravitational field (g = 9.8 N/kg) and then multiplied by the change in height (about 1 meter). This will give a change in energy of about 10 joules. So that gives you a rough feeling for the amount of energy in a joule.
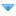
But what about power? Power is the rate of energy change. It tells you how fast you use energy. As an equation, it looks like this:
defpower
In this expression, if ΔE is the change in energy in units of joules and Δt is the time interval in seconds then the power will be in units of watts.
We are almost ready to calculate the vaccine doughnut power. We just need one more estimation—the efficiency. When a human eats a doughnut, only some of the chemical energy goes all the way into useful energy. Also, with a stationary bike generator some of the energy the human uses to push the pedals also goes into heating up some of the moving parts. In the end, only a percentage of the energy goes into electrical energy. This percentage is the efficiency. I'm just going to make a rough guess that the process of doughnut eating to electrical energy is 25 percent efficient.
That's it. I just need to take the number of doughnuts per day and convert that energy to joules and then divide by the length of a day (in seconds). Oh, and multiply by the efficiency. Here's what I get. Note: this is actual python code. You can see my calculations and even change them if you like.
pythonpower
You can see that for each human, it's just a measly 2 watts of power. That's around the power output for a smart phone (power values vary based on use). However, once you include all the vaccinated people we get up to 144 Megawatts. In 2019, the average household power was about 1200 watts. That means that you could use all these doughnuts to run 120 thousand homes. Oh, AND you get vaccinated—that's a win.
More Great WIRED Stories
? The latest on tech, science, and more: Get our newsletters!
When the boss of all dating apps met the pandemic
Get moving with our favorite fitness apps and services
Why covering canals with solar panels is a power move
How to keep nearby strangers from sending you files
Help! Should I tell my colleagues I’m on the spectrum?
?️ Explore AI like never before with our new database
? WIRED Games: Get the latest tips, reviews, and more
??♀️ Want the best tools to get healthy? Check out our Gear team’s picks for the best fitness trackers, running gear (including shoes and socks), and best headphones
https://www.wired.com/story/how-many-hom...-doughnuts
Should you get a COVID vaccine? Yes, it will protect you AND protect others to help us move past this pandemic so we can get back to a more normal life. But wait! If you get vaccinated, you can also get a doughnut! At least that's the deal that Krispy Kreme Doughnuts is offering. Once you get your vaccine, you get a doughnut. Oh, it's not just one doughnut—it's one doughnut every day. That's a lot of doughnuts.
OK, so how about some physics estimations to go along with your tasty doughnut?
Let's say that all the Americans that have a COVID vaccine get (and eat) one doughnut a day. Of course eating food gives you energy to do stuff—that's how food works. So, suppose that all these humans eat their doughnut and then use the extra energy to peddle a stationary bike. All of these bikes are then connected to generators so that they feed into the power grid. What kind of power output would this produce?
The first thing we need is the number of doughnuts a day. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC) 63 million Americans have been fully vaccinated so far (as of April 7 2021). Oh, don't worry too much about the numbers—I'm going to do all my calculations in python so that you can change the values if that makes you happy. I'm also going to assume that all these people get their doughnut—every day.
Next, I need to know the amount of energy per doughnut. According to Krispy Kreme's site, a plain glazed doughnut is 190 Calories. But what the heck is a Calorie? Well, [the original calorie was created to describe changes in thermal energy for different substance](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calories. Then, later people used it to measure the amount of chemical energy your body can get from eating food. However, there is a problem. For some reason, all food labels list stuff in Calories—but these are really kilocalories. So, that doughnut has 190,000 calories. I guess it just sounds like it's too big of a number for people to consider eating.
There is another unit of energy—the joule. Since this is the preferred unit of energy for physicists, I'm going to use it. To convert between units, 1 calorie is equal to 4.184 joules. But what does this have to do with your everyday life? Let's consider something you might do without too much effort. Suppose you have a textbook on the floor and you pick it up to put it on a table. Since you are exerting a force on the book over some distance, you have to change the gravitational potential energy of that book. The change in gravitational potential energy is equal to the mass of the book (about 1 kilogram) multiplied by the local gravitational field (g = 9.8 N/kg) and then multiplied by the change in height (about 1 meter). This will give a change in energy of about 10 joules. So that gives you a rough feeling for the amount of energy in a joule.
But what about power? Power is the rate of energy change. It tells you how fast you use energy. As an equation, it looks like this:
defpower
In this expression, if ΔE is the change in energy in units of joules and Δt is the time interval in seconds then the power will be in units of watts.
We are almost ready to calculate the vaccine doughnut power. We just need one more estimation—the efficiency. When a human eats a doughnut, only some of the chemical energy goes all the way into useful energy. Also, with a stationary bike generator some of the energy the human uses to push the pedals also goes into heating up some of the moving parts. In the end, only a percentage of the energy goes into electrical energy. This percentage is the efficiency. I'm just going to make a rough guess that the process of doughnut eating to electrical energy is 25 percent efficient.
That's it. I just need to take the number of doughnuts per day and convert that energy to joules and then divide by the length of a day (in seconds). Oh, and multiply by the efficiency. Here's what I get. Note: this is actual python code. You can see my calculations and even change them if you like.
pythonpower
You can see that for each human, it's just a measly 2 watts of power. That's around the power output for a smart phone (power values vary based on use). However, once you include all the vaccinated people we get up to 144 Megawatts. In 2019, the average household power was about 1200 watts. That means that you could use all these doughnuts to run 120 thousand homes. Oh, AND you get vaccinated—that's a win.
More Great WIRED Stories
? The latest on tech, science, and more: Get our newsletters!
When the boss of all dating apps met the pandemic
Get moving with our favorite fitness apps and services
Why covering canals with solar panels is a power move
How to keep nearby strangers from sending you files
Help! Should I tell my colleagues I’m on the spectrum?
?️ Explore AI like never before with our new database
? WIRED Games: Get the latest tips, reviews, and more
??♀️ Want the best tools to get healthy? Check out our Gear team’s picks for the best fitness trackers, running gear (including shoes and socks), and best headphones
https://www.wired.com/story/how-many-hom...-doughnuts









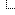
![[-] [-]](https://www.chinaphonearena.com/forum/images/collapse.png)

